
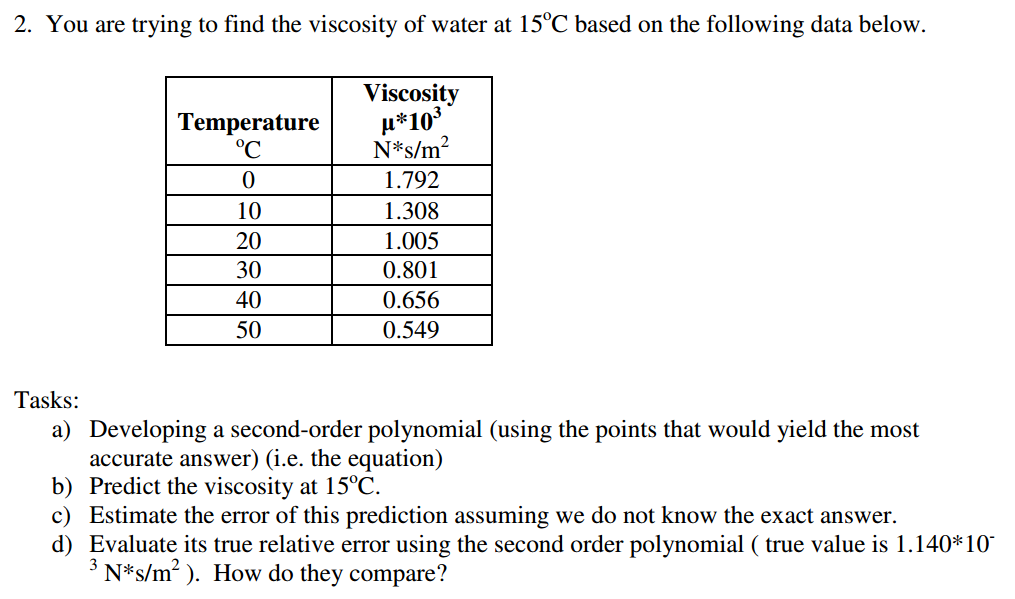
The fluid layers in between the plates slide parallel to one another on account of molecules having different momentum crossing the fluid layers. Kinematic Viscosity The ratio of the absolute viscosity of a liquid to its density frequently occurs in the study of viscosity and hydraulics and the term 'kinematic viscosity' with the symbol V has been.The fluid layer in contact with the upper plate will move with velocity u and the fluid layer in contact with the lower plate, which is at rest will not move and will have zero velocity. The internationally agreed standard for viscosity, ISO/T R 3666:1998, is the viscosity of water at 20 C and atmospheric pressure (0.The viscosity of a fluid is used to describe how difficult it is for a fluid to flow and how difficult it is for an object to move through a fluid. The viscosity of water changes with its temperature, and the greater the temperature, the less viscous the water becomes. both tubes at room temperature(20 C) with little to no fluctuation in heat. Now let the upper plate be moved by a force F. At 20 C, waterhas a viscosity of 1.0016 millipascals per second. Finding viscosity of a liquid by measuring velocity of small balls sinking.Consider a fluid which is at rest between the solid surfaces, separated by small distance Δy, along the y-direction, and extended infinitely in the other direction.All fluids possess viscosity though to varying degree. This property is on account of cohesion and interaction between its molecules, which causes resistance to tangential or shear stress.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
